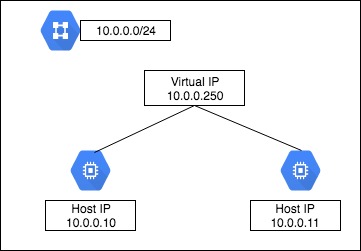
GCEでは、単一インスタンスに同一ネットワークのIPアドレスを複数持たせる事ができない。
複数のネットワーク インターフェースの概要と例
つまり、Virtual IPを同一セグメントに持たせた構成は出来ない。
クラスタを組みたかったけど、今回の要件としては
1. Active/Standbyの構成にする
2. Activeのpostgresが止まった場合、Standbyを昇格する
3. フェイルバックは行わない。
4. フェイルオーバー後、App側で検知。
必要な設定変更後、動的にサービスの再起動を行う。
5. 1分以内にサービスが復旧される。
とシンプルな構成にする。
PostgreSQL
要件1、2には、pg_keeperを使う。
クラスタでは無いのでスプリットブレインの検知などは出来ない。
その為、アプリケーション側に今のActive機の情報を教える必要がある。
スプリットブレイン対策用のDB、Table作成
postgres=# create database pg_state;
postgres=# create table failover_log (unixtime int, host varchar(10));
インストール(Actice/Standby共に)
cd /usr/local/src
git clone https://github.com/MasahikoSawada/pg_keeper.git
export PATH=/usr/pgsql-9.6/bin/:$PATH
make USE_PGXS=1
make USE_PGXS=1 install
postgresql.conf書き換え(Actice/Standby共に)
vim postgresql.conf
shared_preload_libraries = 'pg_keeper'
pg_keeper.my_conninfo = 'host=10.0.0.10 port=5432 dbname=postgres'
pg_keeper.partner_conninfo = 'host=10.0.0.11 port=5432 dbname=postgres'
pg_keeper.keepalive_time = 2
pg_keeper.keepalive_count = 3
pg_keeper.after_command = 'sleep 1 ; psql -d pg_state -c "insert into failover_log values(`date +%s`, \'`hostname`\');" -x'
Activeが止まった場合、pg_keeper.keepalive_time秒 × pg_keeper.keepalive_count回 チェックを行い、全てNGの場合にフェイルオーバーを実行し、最後にpg_keeper.after_commandの内容が実行される。
今回は、フェイルオーバー後に[unixtimestamp, hostname]を pg_state.failover_logに入れている。
app側
これはアプリケーションのよるので参考まで。
monitor_master_db.pyというモニタリングスクリプトを作成し、root権限で動かす事にした。
動きとしては、Active/Standby両機のDBのpg_state.failover_logをチェックし、タイムスタンプが若い方をDB接続先として、設定ファイル(yaml)を書き換えデーモンの再起動を行う。
#!/bin/env python3
import os,sys
import yaml
import psycopg2
import codecs
import subprocess
yaml_file = '/PATH/TO/env.yaml'
dbs = ['postgresql://postgres@db01:5432/pg_state'
,'postgresql://postgres@db02:5432/pg_state']
def get_item():
arr = []
for db in dbs :
try:
dbcon = psycopg2.connect(db)
cur = dbcon.cursor()
cur.execute('select * from failover_log order by unixtime desc limit 1')
result = cur.fetchone()
cur.close()
dbcon.close()
arr.append(result)
except :
pass
if len(dbs) == len(arr): # Active/Standby共にデータ取得成功
if arr[0][0] > arr[1][0]:
return arr[0][1]
else :
return arr[1][1]
else : # 片系が停止している
return arr[0][1]
def overwrite(db_name):
with codecs.open(yaml_file, 'r', 'utf-8') as read :
env_dict = yaml.load(read)
if env_dict['db_master'][0]['address'] != '{}:5432'.format(db_name) or env_dict['db_slave'][0]['address'] != '{}:5432'.format(db_name):
env_dict['db_master'][0]['address'] = '{}:5432'.format(db_name)
env_dict['db_slave'][0]['address'] = '{}:5432'.format(db_name)
with codecs.open(yaml_file, 'w', 'utf-8') as write :
yaml.dump(env_dict, write, encoding='utf8', allow_unicode=True, default_flow_style=False)
try:
subprocess.check_call(["systemctl", "restart", "デーモン"])
except :
pass
作成したmonitor_master_db.pyをcronで動かす。
cronは普通に書くと1分が最小の実行単位だが、以下のように書くと5秒単位でスクリプトを実行してくれる。
# 5秒間隔
* * * * * for i in `seq 1 12`;do sleep 5; python3 /usr/local/bin/monitor_master_db.py; done
# 10秒間隔の場合
* * * * * for i in `seq 1 6`;do sleep 10; python3 /usr/local/bin/monitor_master_db.py; done
この状態で、Active側のDBを落として、フェイルオーバーされApp側の接続先も変更される事を確認する。
Slave側が昇格前にfailover_logへのinsertが実行される場合、pg_keeper.after_commandのsleepを大きくする。
pg_keeper.after_command = 'sleep 5 ; psql -d pg_state -c "insert into failover_log values(`date +%s`, \'`hostname`\');" -x'